Bronchiectasis without lower respiratory symptoms in the presence of multisystem anomalies – a clinical clue to diagnose esophageal lung anomaly
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
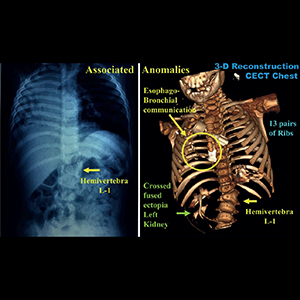
Esophageal lung is a type of Group-II communicating bronchopulmonary foregut malformations (CBPFM) usually diagnosed beyond neonatal period during investigation for recurrent respiratory symptoms and persistent radiographic features suggesting pneumonia or bronchiectasis. In our case, we noticed bronchiectasis and disproportionately severe volume loss in an infant with associated multisystem anomalies in the absence of “significant” lower respiratory tract symptoms. A detailed evaluation with repeat imaging confirmed a Group-II CBPFM, a congenital pathology instead of an infective cause. Pneumonectomy is a more prudent option instead of undertaking major airway reconstruction for the dysplastic “dysfunctional” tissue. Amongst the various associated anomalies reported till now, the associated rib and renal anomalies noted by us have not been described earlier to the best of our knowledge.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






