Two years progression-free survival under vinorelbine metronomic therapy of a patient with metastatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
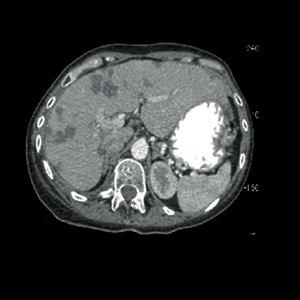
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE) is a very rare vascular tumor, originating from endothelial cells. The etiology of EHE is unknown, yet at the molecular level, different angiogenic stimulators may act as promoters of endothelial cell proliferation. The tumor affects more commonly the lung, the liver and the bones but it can affect any other organ. Due to its heterogeneous presentation and its rarity it is often misdiagnosed. No treatment is proved to be efficient in metastatic EHE and the median survival of patients with metastatic pleural disease is generally poor, less than one year. we report a case of a 57-year-old female with multiple metastatic EHE including pleural, diagnosed by medical thoracoscopy, with a progression-free survival of 24 months with oral vinorelbine as maintenance therapy after combination of cisplatin-vinorelbine. We believe that this therapy might be of value to test in this patient population as it has never been tested before.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






