Exertional and nocturnal periodic breathing after successful cardiac transplantation. A case report
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
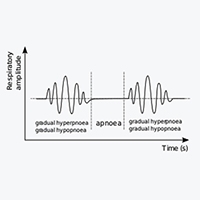
We present a case report of a heart failure patient who underwent cardiopulmonary exercise testing and sleep screening 12 months before and after heart transplantation (HTx). Severe Cheyne-Stokes respiration (CSR) with central sleep apnoea (CSA) was identified either before and after HTx, while periodic breathing during exercise vanished. We suggest that optimization of hemodynamics and medical therapy (low dose of diuretic) did not withdraw the central mechanisms underlying the diathesis for CSR-CSA. While periodic breathing during exercise reversal may support a closer link with an exertional central hemodynamic. This observation indirectly neglects the possible unifying mechanistic background of CSR and periodic breathing, during exercise, in this setting.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






